Macoma balthica (Linnaeus, 1758)
Baltic macomaWarning: DOMDocument::load(): SSL operation failed with code 1. OpenSSL Error messages: error:140770FC:SSL routines:SSL23_GET_SERVER_HELLO:unknown protocol in C:\Apache24\htdocs\includes\SpeciesSummary.lib.php on line 1236
Warning: DOMDocument::load(): Failed to enable crypto in C:\Apache24\htdocs\includes\SpeciesSummary.lib.php on line 1236
Warning: DOMDocument::load(https://sealifebase.nrm.se/webservice/AquaMaps/getAMap.php?genus=Macoma&species=balthica): failed to open stream: operation failed in C:\Apache24\htdocs\includes\SpeciesSummary.lib.php on line 1236
Warning: DOMDocument::load(): I/O warning : failed to load external entity "https://sealifebase.nrm.se/webservice/AquaMaps/getAMap.php?genus=Macoma&species=balthica" in C:\Apache24\htdocs\includes\SpeciesSummary.lib.php on line 1236
Upload your photos
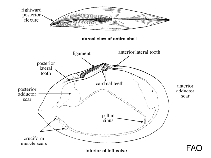
Google image | No image available for this species;
drawing shows typical species in Tellinidae.
Google image | No image available for this species;
drawing shows typical species in Tellinidae.
Classification / Names Common names | Synonyms | CoL | ITIS | WoRMS
Bivalvia | Cardiida | Tellinidae
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range Ecology
Benthic; brackish; depth range 0 - 270 m (Ref. 95344). Polar
Distribution Countries | FAO areas | Ecosystems | Occurrences | Introductions
Arctic, Northern Atlantic, Northeast Pacific and the Mediterranean Sea.
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm Max length : 3.8 cm SHL male/unsexed; (Ref. 95344); max. reported age: 10 years (Ref. 2823)
Maximum depth from Ref. 117961. Occurs from the upper part of the intertidal down to the shallow subtidal zone (Ref. 76547). Circumboreal and panarctic. Buries shallow to 20 cm under muddy-sandy substrate, commonly in bays and estuaries (Refs. 95344, 95753). In the northern Baltic Sea, known to thrive in eutrophic conditions (Ref. 95752). It is infaunal on sand and eelgrass beds and epifaunal on eelgrass beds (Ref. 95819). Deposit and suspension feeder (Refs. 76547, 96470). Surface deposit feeder (Ref. 66387). Feeds from the surface of the sediment using their long siphons (Ref. 7882), and is a subsurface detritivore (Refs. 95728, 96470).
Life cycle and mating behavior Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Members of the class Bivalvia are mostly gonochoric, some are protandric hermaphrodites. Life cycle: Embryos develop into free-swimming trocophore larvae, succeeded by the bivalve veliger, resembling a miniature clam.
Main reference
References | Coordinator | Collaborators
Vakily, J.M. 1992. (Ref. 7693)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435)
CITES status (Ref. 108899)
Not Evaluated
CMS (Ref. 116361)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Human uses
| FishSource |
Tools
More information
Internet sources
BHL | BOLD Systems | CISTI | DiscoverLife | FAO(Publication : search) | Fishipedia | GenBank (genome, nucleotide) | GloBI | Gomexsi | Google Books | Google Scholar | Google | PubMed | Tree of Life | Wikipedia (Go, Search) | Zoological Record
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature
(Ref. 115969): 5.3 - 14.2, mean 9.7 (based on 850 cells).
Resilience
(Ref. 69278):
Medium, minimum population doubling time 1.4 - 4.4 years (K=0-0.46; tmax=10).
Price category
(Ref. 80766):
Unknown.