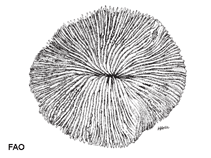
Fungia fungites (Linnaeus, 1758)
Common mushroom coralWarning: DOMDocument::load(http://sealifebase.nrm.se/webservice/AquaMaps/getAMap.php?genus=Fungia&species=fungites): failed to open stream: HTTP request failed! in C:\Apache24\htdocs\includes\SpeciesSummary.lib.php on line 1236
Warning: DOMDocument::load(): I/O warning : failed to load external entity "http://sealifebase.nrm.se/webservice/AquaMaps/getAMap.php?genus=Fungia&species=fungites" in C:\Apache24\htdocs\includes\SpeciesSummary.lib.php on line 1236
Classification / Names Common names | Synonyms | CoL | ITIS | WoRMS
Anthozoa | Scleractinia | Fungiidae
Environment: milieu / climate zone / depth range / distribution range Ecology
Reef-associated; depth range 3 - 20 m (Ref. 8294). Tropical; 36°N - 31°S, 32°E - 137°W (Ref. 847)
Distribution Countries | FAO areas | Ecosystems | Occurrences | Introductions
Indo-Pacific.
Length at first maturity / Size / Weight / Age
Maturity: Lm ? range ? - ? cm Max length : 30.0 cm COLD male/unsexed; (Ref. 269)
Short description Morphology
The coral is circular in outline, up to 30 cm in diameter. The upper surface is fairly rough due to moderate to deeply incised septal dentations on most septocostae, and the lower surface is rough due to costal spines (Ref. 269). The coral is circular in outline, up to 30 cm in diameter.
Maximum depth from Ref. 98471. Found at intermediate depths on reef slopes (Ref. 269). Also on back reefs, reef flats, and lagoons. Solitary, free-living (Ref. 98471).
Life cycle and mating behavior Maturity | Reproduction | Spawning | Eggs | Fecundity | Larvae
Mature gametes are shed into the coelenteron and spawned through the mouth. Life cycle: The zygote develops into a planktonic planula larva. Metamorphosis begins with early morphogenesis of tentacles, septa and pharynx before larval settlement on the aboral end (Ref. 833).
Main reference
References | Coordinator | Collaborators
Hodgson, G. 1998. (Ref. 269)
IUCN Red List Status (Ref. 130435)
Near Threatened (NT) ; Date assessed: 03 January 2008
CITES status (Ref. 108899)
Appendix II: International trade monitored
CMS (Ref. 116361)
Not Evaluated
Threat to humans
Human uses
| FishSource |
Tools
More information
Internet sources
BHL | BOLD Systems | CISTI | DiscoverLife | FAO(Publication : search) | Fishipedia | GenBank (genome, nucleotide) | GloBI | Gomexsi | Google Books | Google Scholar | Google | PubMed | Hexacorallians of the World | Tree of Life | Wikipedia (Go, Search) | Zoological Record
Estimates based on models
Preferred temperature
(Ref. 115969): 25.4 - 29.3, mean 28.6 (based on 2495 cells).
Price category
(Ref. 80766):
Unknown.